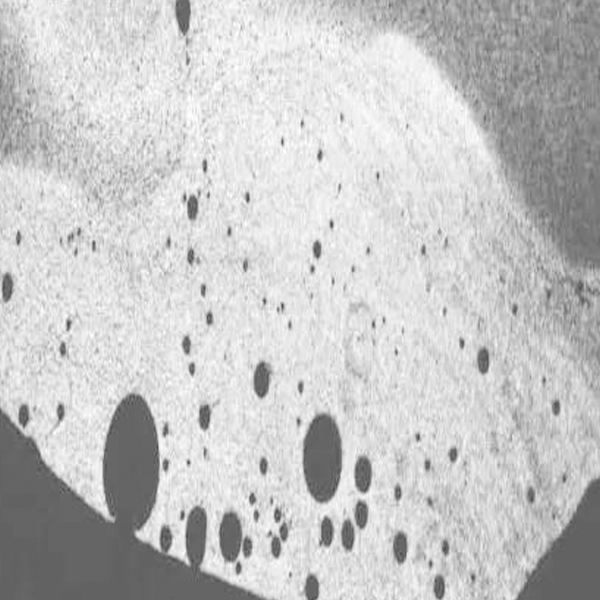
- Gas trapped during Casting:
- During the die casting process, gases can be entrapped in the molten metal. These trapped gases can result in porosity in the casting, and the anodizing process may highlight or emphasize these pores.
- Alloy Composition:
- The composition of the aluminum die casting alloy can influence porosity. Certain alloying elements, such as silicon, may contribute to the formation of gas porosity if not properly controlled during the casting process.
- Casting Parameters:
- Improper casting parameters, such as injection speed, pressure, and temperature, can lead to the formation of porosity. Rapid cooling or improper venting in the die can contribute to gas entrapment.
- Die Design and Venting:
- Inadequate venting in the die casting mold can result in trapped gases, leading to porosity. Proper die design, including venting systems, is crucial to minimize this issue.
- Casting Quality and Porosity Inspection:
- The initial quality of the casting, including the presence of microstructural defects and pores, can affect the anodizing process. Porosity that is not visible to the naked eye may become apparent after anodizing.
- Anodizing Process Conditions:
- Anodizing conditions, such as the type of electrolyte, temperature, and voltage, can influence the appearance of pores on the anodized surface. Improper process parameters may exacerbate the visibility of existing porosity.
- Sealing Process:
- If the anodized part undergoes a sealing process to close the pores in the oxide layer, the effectiveness of the sealing process can impact the final porosity.
- Alloying Elements:
- Certain alloying elements, such as zinc and copper, can contribute to the formation of porosity during the die casting process. These elements may react with the electrolyte during anodizing and affect the appearance of pores.
To address and minimize porosity, it is essential to optimize the die casting process parameters, use suitable alloys, and implement effective quality control measures. Additionally, collaboration between die casters and anodizing specialists is crucial to achieving the desired finish while minimizing the visibility of pores on the anodized surface.