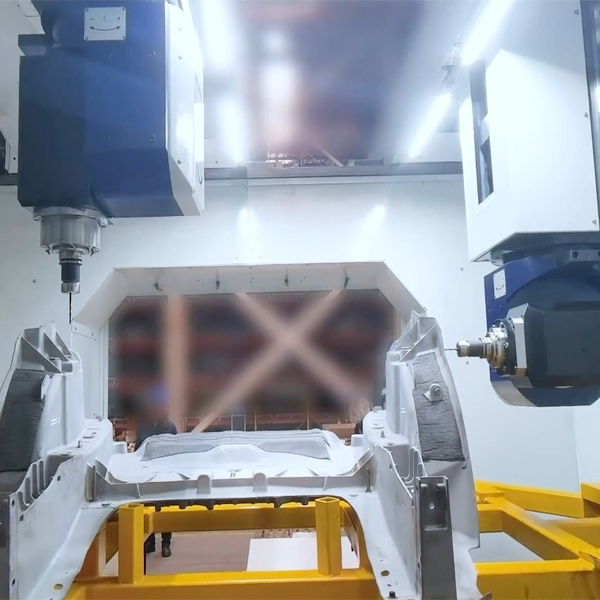
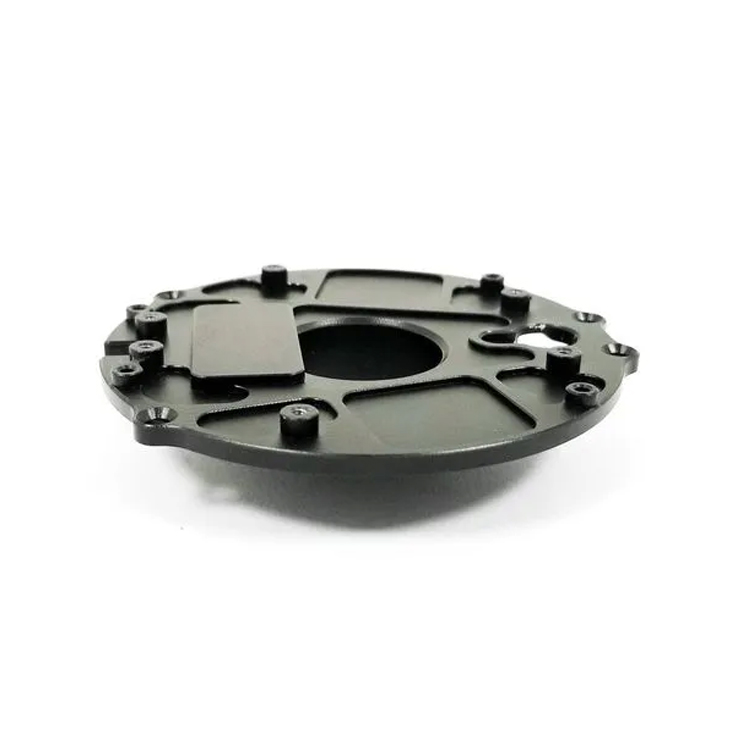
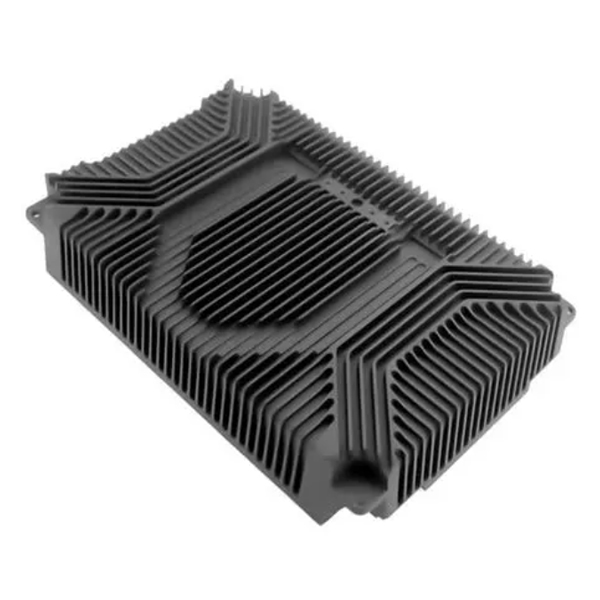
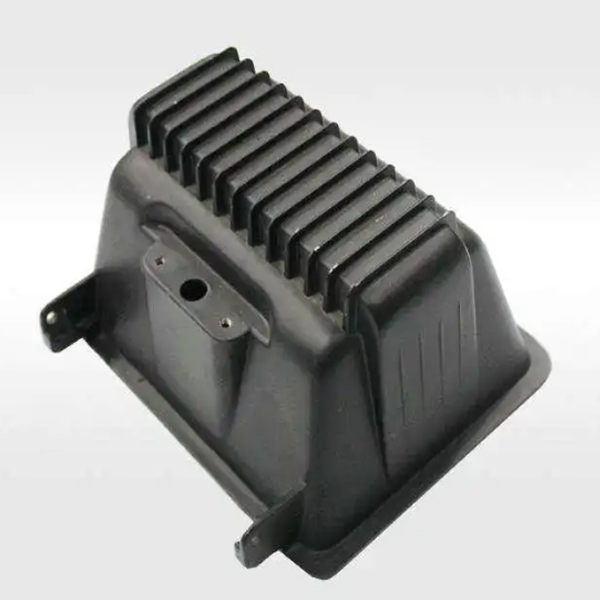
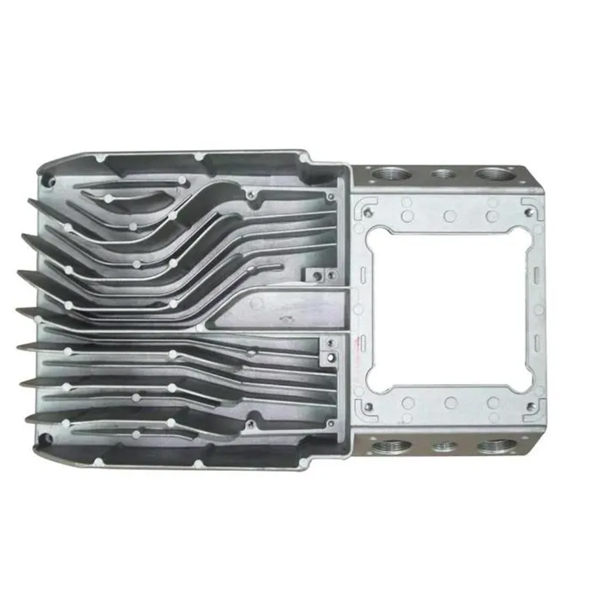
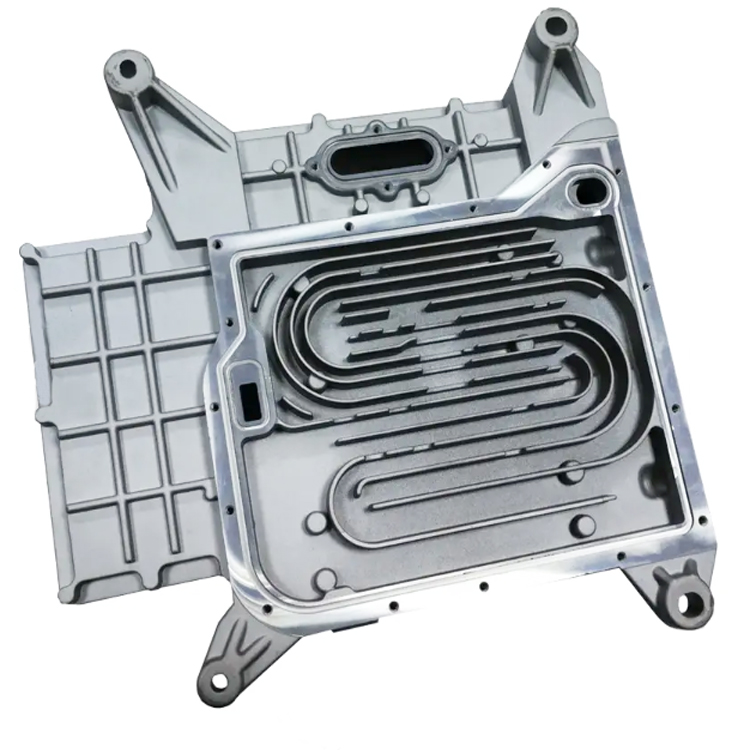
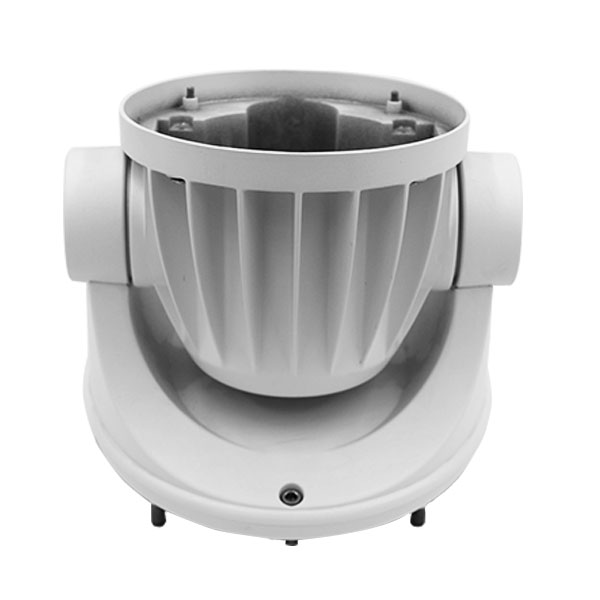
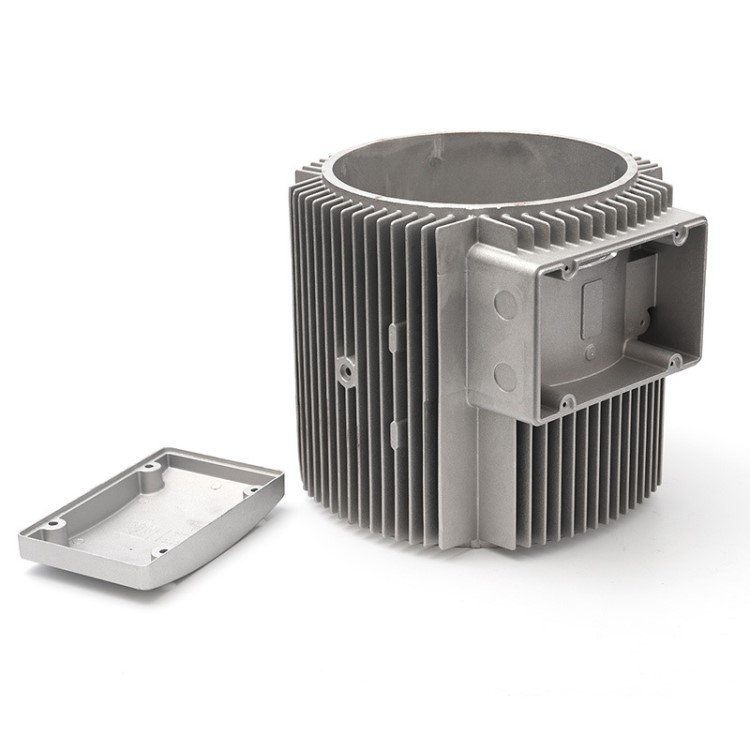
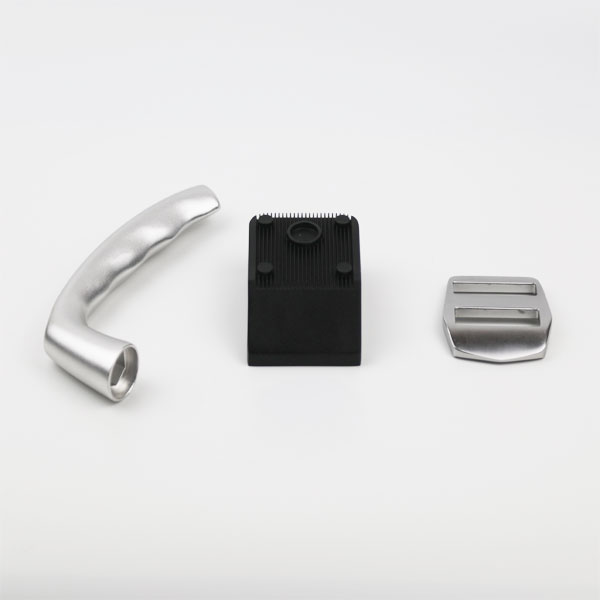
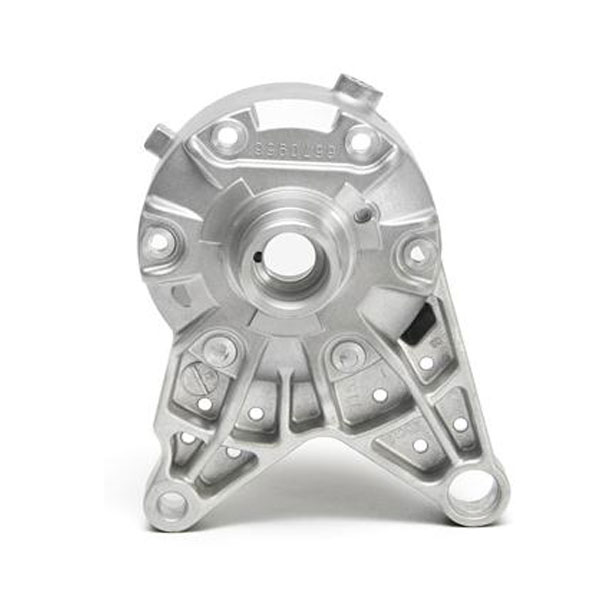
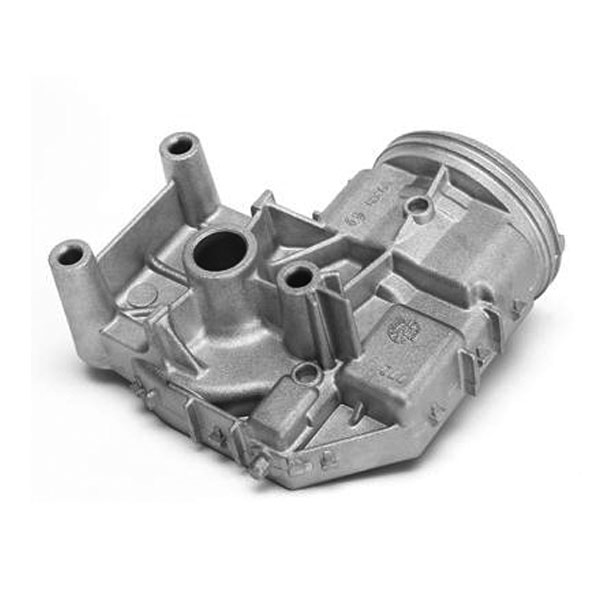
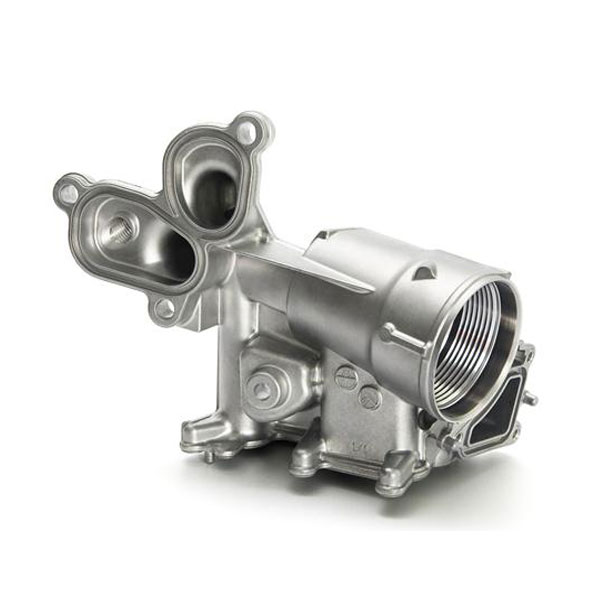
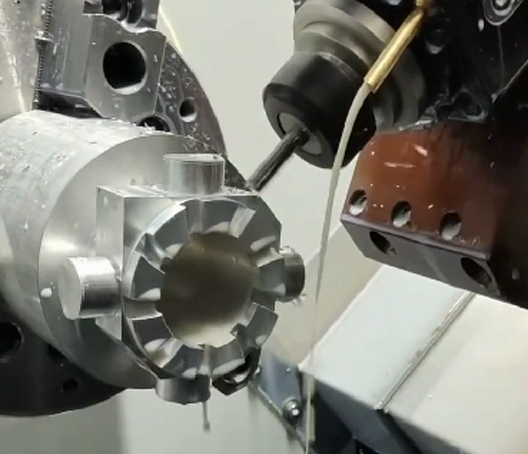
- Milling:
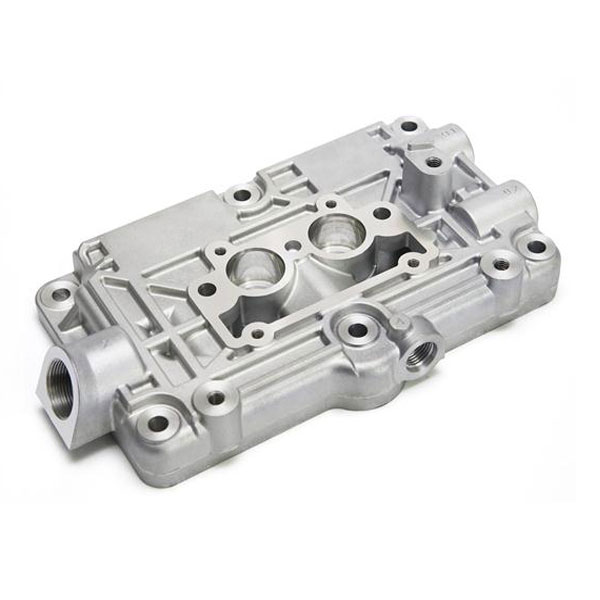
- Face Milling: Used to create flat surfaces on the die-cast part.It is most common machining process for aluminum die casting parts.
- Peripheral Milling: Involves removing material from the periphery of the part.
- Pocket Milling: Used for machining pockets or enclosed areas.It is rarely used for aluminum die casting parts since the slot or pocket can be directly made by die casting tooling.
- Turning:
- CNC Turning: Suitable for cylindrical parts, turning is effective for creating grooves, threads, and contours.To improve precision of gasket groove of die casting parts,turning is most cost effective process.
- Drilling:
- Hole Machining: Essential for creating holes of various diameters.For small hole less than 5mm diameter,drilling will be better than directly made via die casting tooling.
- Tapping:
- Thread Machining: Adding threads to holes using tapping processes.Tapping can be done by mannual machine or CNC according to process volume.
- Grinding:
- Surface Grinding: Achieves a smooth finish on flat surfaces.
- Cylindrical Grinding: For creating cylindrical shapes or improving concentricity.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining):
- Wire EDM: Used for intricate shapes and tight tolerances.
- Sink EDM: Ideal for creating complex 3D geometries.
- Laser Machining:
- Laser Cutting: Precise cutting for specific shapes.
- Laser Engraving: Adding marks or features on the surface.
- Deburring:
- Remove Burrs: Post-machining process to eliminate sharp edges or burrs left from casting.
- Surface Treatment:
- Anodizing: Enhances corrosion resistance and provides a decorative finish.
- Painting/Coating: Adds aesthetic appeal and protects against corrosion.
- Chemical Conversion Coating: Improves corrosion resistance and adhesion of paint.
- Assembly:
- Joining Components: Machined parts may need to be assembled with other components to form the final product.
When machining aluminum die casting parts, it’s essential to consider the material properties of aluminum, such as its relatively low melting point, heat conductivity, and potential for chip formation. Proper tool selection, cutting speeds, and feeds are crucial to achieving optimal machining results. Additionally, using coolant/lubrication during machining can help control temperatures and improve tool life.